すべてはシュタインズゲートの選択だ1. Introduction 2015-06-22
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Fingerprint Authentication System
Fingerprint identification system is an important identity authentication system. It will be more and more important in modern society. Traditional fields such as security system, access control system must use this technology. With the rise of the mobile Internet, more and more emerging fields such as e-commerce, electronic payment also need this technology.
The traditional fingerprint recognition system adopts the following technical architecture: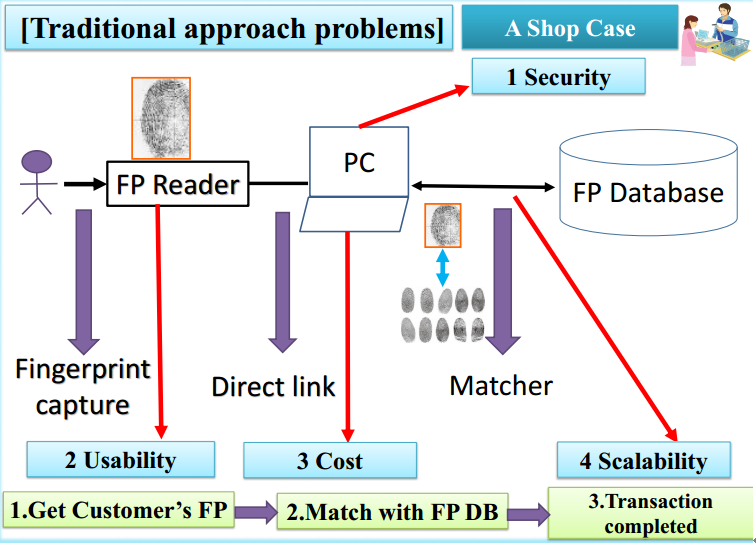
The business process is as follows:
- Users press the fingerprints on the fingerprints sensor.
- The sensor is connected to the computer system and sends the user’s fingerprints directly to the computer system.
- The similarity of fingerprint data between user and database will be compared.
- The fingerprint authentication system judges whether the user is authenticated by the similarity and returns the result to the user.
However, with the rise of mobile Internet, the drawbacks of this traditional fingerprint authentication system were exposed. First is security issue, the user fingerprint data stored directly in the system computer, user’s fingerprint image information is easy to be stolen; Second is usability and cost issues, the traditional fingerprint system requires sensor to input users’ fingerprints and the system deployment requires a separate terminal hardware and terminal software. All these lead to increased costs and decreased usability. Third is a scalability issue, the architecture of host-database is not easy to extend. Once scenarios need to use the system, we must purchase the corresponding hardware and software, leading to poor scalability.
In this paper, the drawbacks of traditional fingerprint identification system has been improved and reorganized. We developed a web-based fingerprint authentication system using smartphone, and used a number of security defense strategies to enhance the security of the system. Finally, the new approach can solve the security, usability, cost and scalability issues in the traditional fingerprint identification system.
System architecture is as follows: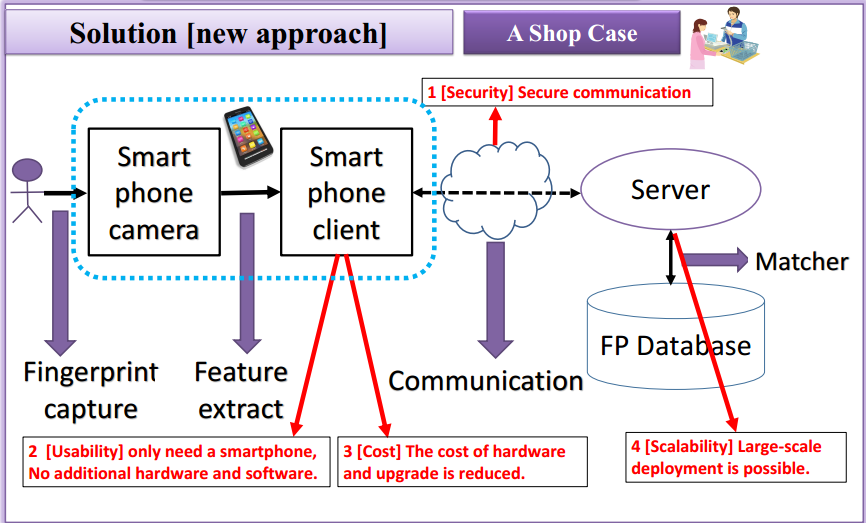
The innovation of the system is:
- Using smartphone camera instead of the traditional fingerprint sensor, to solve the cost and usability issues.
- Using Web Service to provide cross-platform service to solve the cost and scalability issues.
- Using enhanced security defense strategy, to solve the security issue.
This paper focuses on the server solution based on enhanced security strategy.
1.2 Security Threat
The following security threat will occur in the web-based fingerprint authentication system:
1.2.1 Intercept Information
The purpose of intercepting information is to steal data content itself. This type of security threat is commonly referred to as data security threats. In the fingerprint authentication system, client needs to send the fingerprint image file to the server through network. During transmission, once the system is attacked, it may cause the fingerprint image data to be intercepted, and then the user information will be stolen.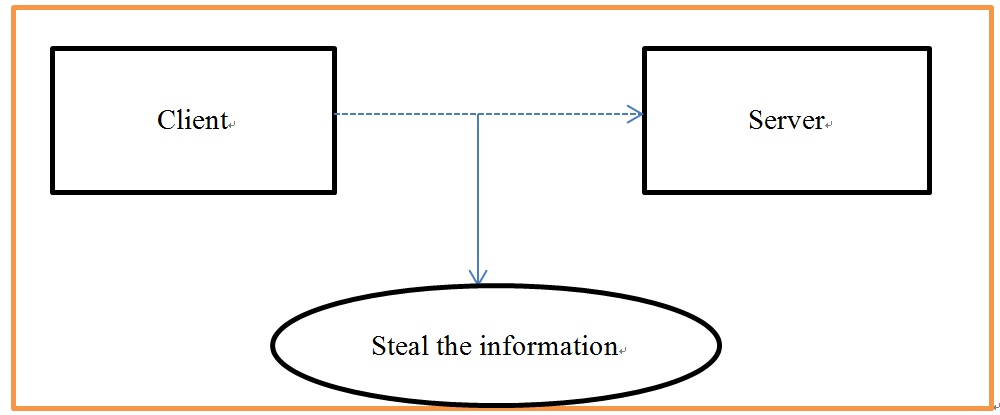
1.2.2 Replay attack
Destroying the validity of certification is a basic form of authentication attack. A replay attack is a form of network attack in which a valid data transmission is maliciously or fraudulently repeated or delayed. This is carried out either by the originator or by an adversary who intercepts the data and retransmits it, possibly as part of a masquerade attack by IP packet substitution.
The classic example of replay attack is as follows: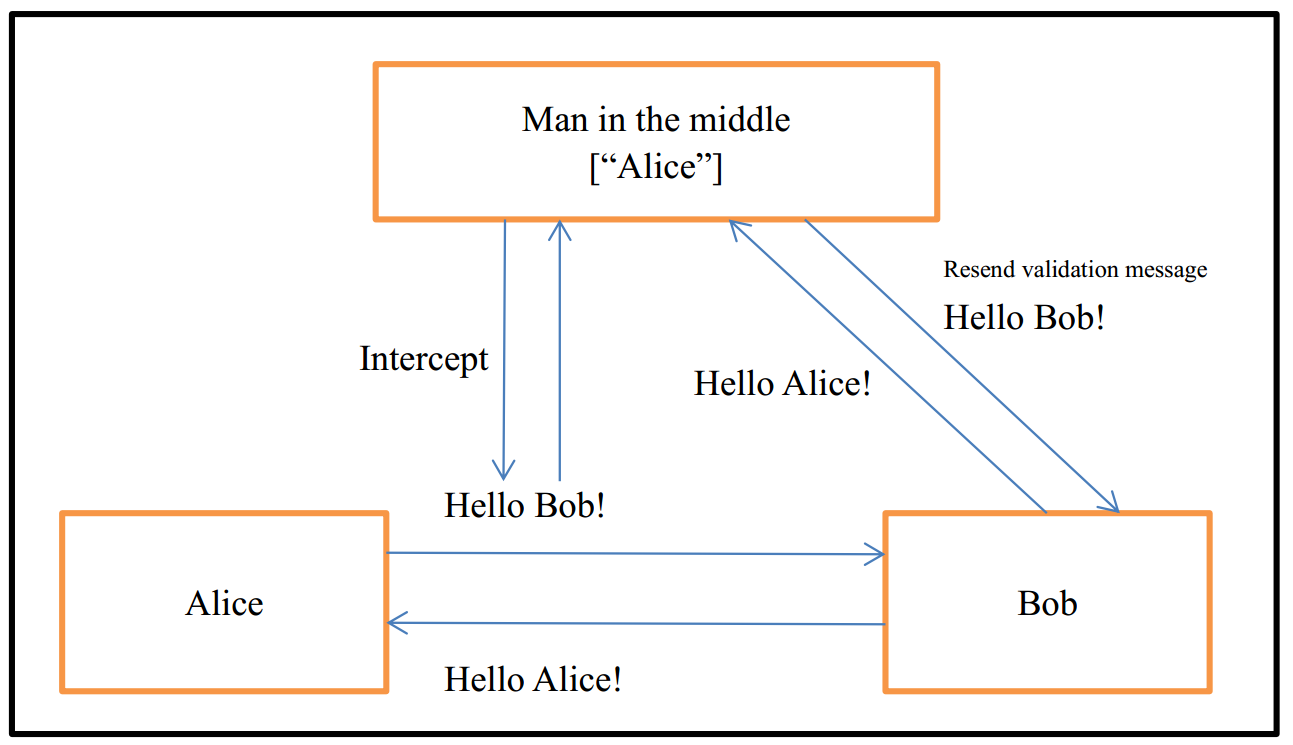
Suppose Alice wants to prove her identity to Bob. Bob requests her password as proof of identity, which Alice dutifully provides (possibly after some transformation like a hash function); meanwhile, Eve is eavesdropping on the conversation and keeps the password (or the hash). After the interchange is over, Eve (posing as Alice) connects to Bob; when asked for a proof of identity, Eve sends Alice’s password (or hash) read from the last session, which Bob accepts thus granting access to Eve.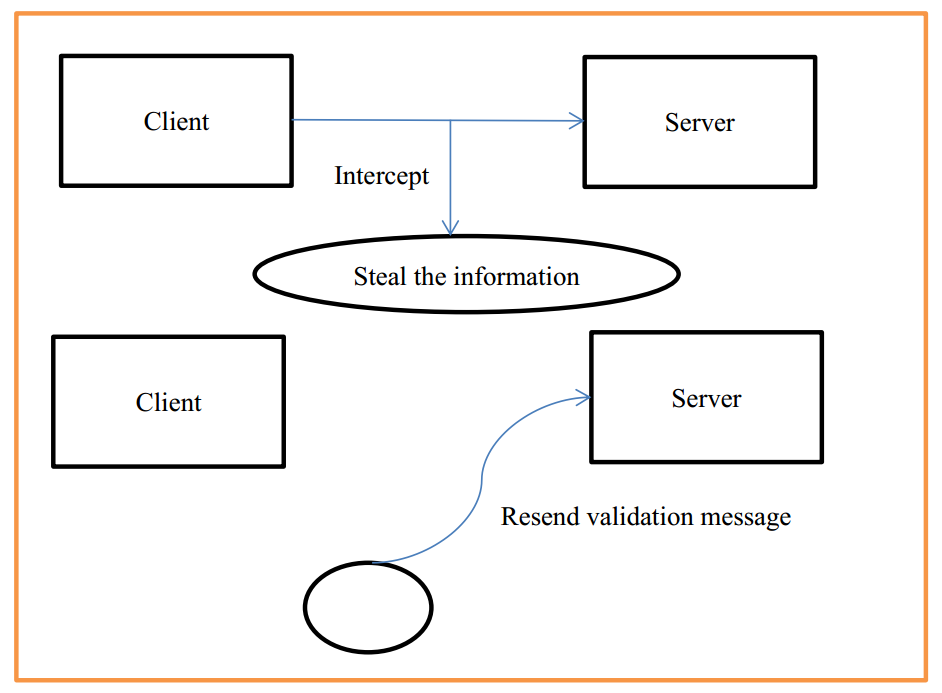
1.2.3 Data Modification
This type of network attacks is an extension of replay attack. Attackers using replay attack damage the system certification to enter the system. Then they can send the forged data to the server easily. And even they will do SQL injection attacks or modify server information. The basic model is as follows: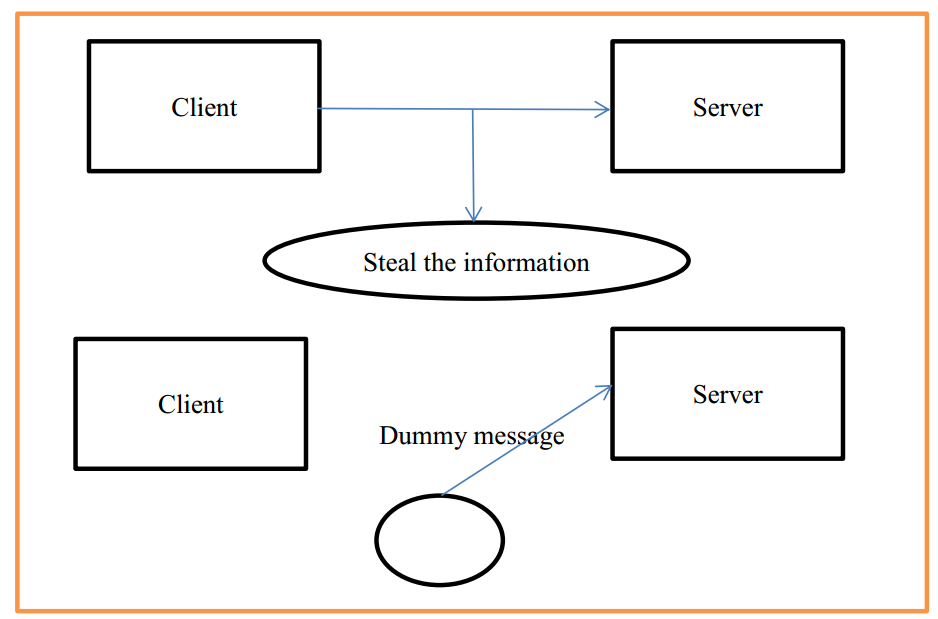
1.3 Defense Strategy
1.3.1 Image Encryption
For attacks in 1.2.1, the usual defense strategy is image encryption. Before the client sends the image file, we can use a specific algorithm to encrypt image. Then client sends the file to the server. After the server receives the file, we will use the same algorithm to decrypt the image. In this case, even if attackers intercept the image file, he still cannot get the real information, thus preventing information leakage.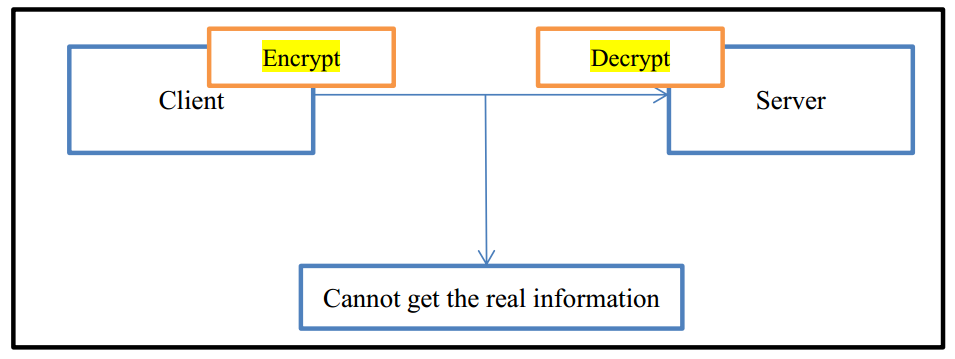
1.3.2 Timestamp Authentication
It is efficient defense against replay attack to add timestamp to the system. To use this approach, we should ensure synchronization between client and server. First, the server generates a dynamic password from time to time. Second, the client sends a request to get the dynamic password. Finally, client sends username and dynamic password to login system. In this case, even if the middle man steal the password, it is only effective in a very short time.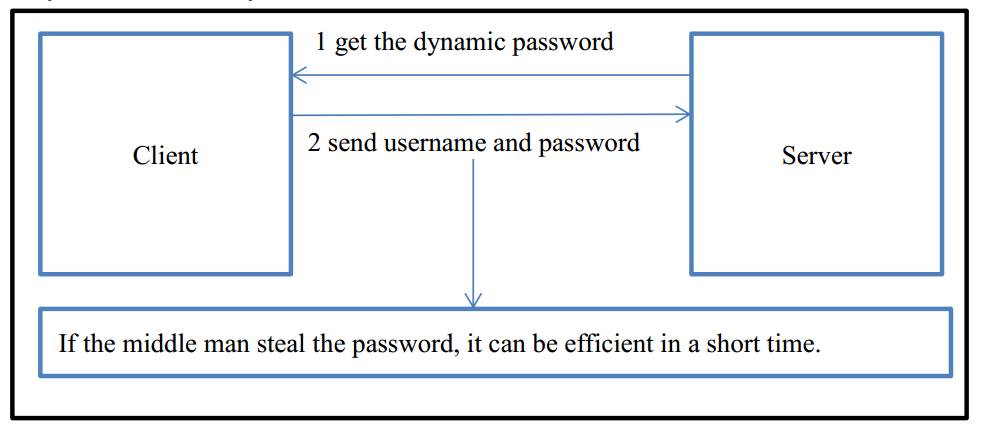
1.3.3 Challenge-Response Authentication
Challenge-Response Authentication is another effective method to prevent replay attack. The basic model is as follows:
- Client sends a request to login. (We can assume it is ‘GET’ request)
- Server generates a random number K=random (NUM), then return K to Client. Besides, server should save K to the session.
- Client calculates R=Hmac(K, P), then sends the result to the server. In the formula, K represents key (the random number), P represents user password, Hmac() is a Hash Function.
- Server gets the user password from database and does the same calculation R’=hmac() as step 3. Then comparing R’ with R, if R’ equals R, users will login system successfully.
In this process, the man in the middle can only get K and R, but K is a random number while R is a hash result, the two numbers are both meaningless. Attackers cannot get user password through the two numbers. System security is improved.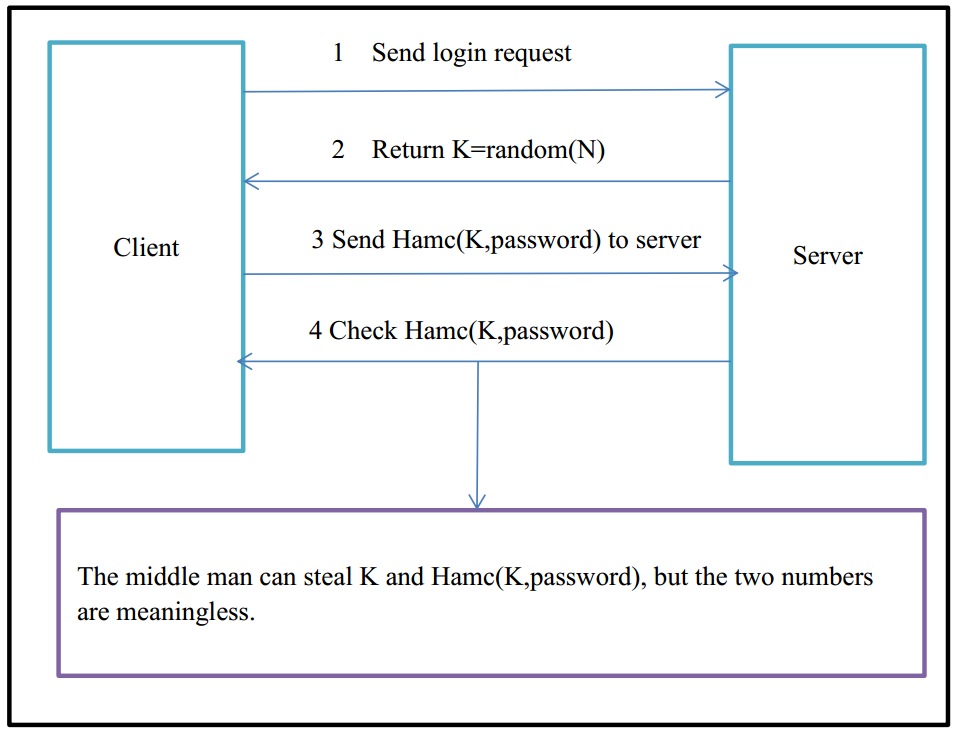
1.4 Fingerprint Authentication System with Enhanced Security
The paper discusses a fingerprint authentication system with enhanced security. First, we will use the new approach to instead of the traditional approach, we will not use fingerprint sensor to get user fingerprint data. Instead, we use smartphone camera to get the user information. It will be more convenient and low cost. Second, we use Web Service to provide web-based authentication service with enhanced security. We use some methods to improve the system security and prevent network attack. Finally, we will realize a new fingerprint authentication system with convenience, security and low cost.
The paper will be divided into 7 chapters.
Chapter 1 expresses the problems of the existed fingerprints authentication system and gives a new approach to solve the problems.
Chapter 2 introduces the related work of fingerprints system and system security.
Chapter 3 gives the system architecture to show how it works.
Chapter 4 discusses the security strategy to prevent network attack.
Chapter 5 discusses fingerprints matcher web service.
Chapter 6 I have no idea now.
Chapter 7 gives the conclusion.